LIPIDS
What are LIPIDS?
It comes from the Greek word "lipos", which means fat. We call it fat if it is solid or oil if it is liquid, depending on ambient temperatures. These compounds are classified as non-polar, meaning they are hydrophobic, or water-fearing, and insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents. The main functions of lipids are for energy storage, for insulation of our bodies and as structural components for cell membranes. Lipids are a composition of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen elements. It is made up of fatty acid monomers.
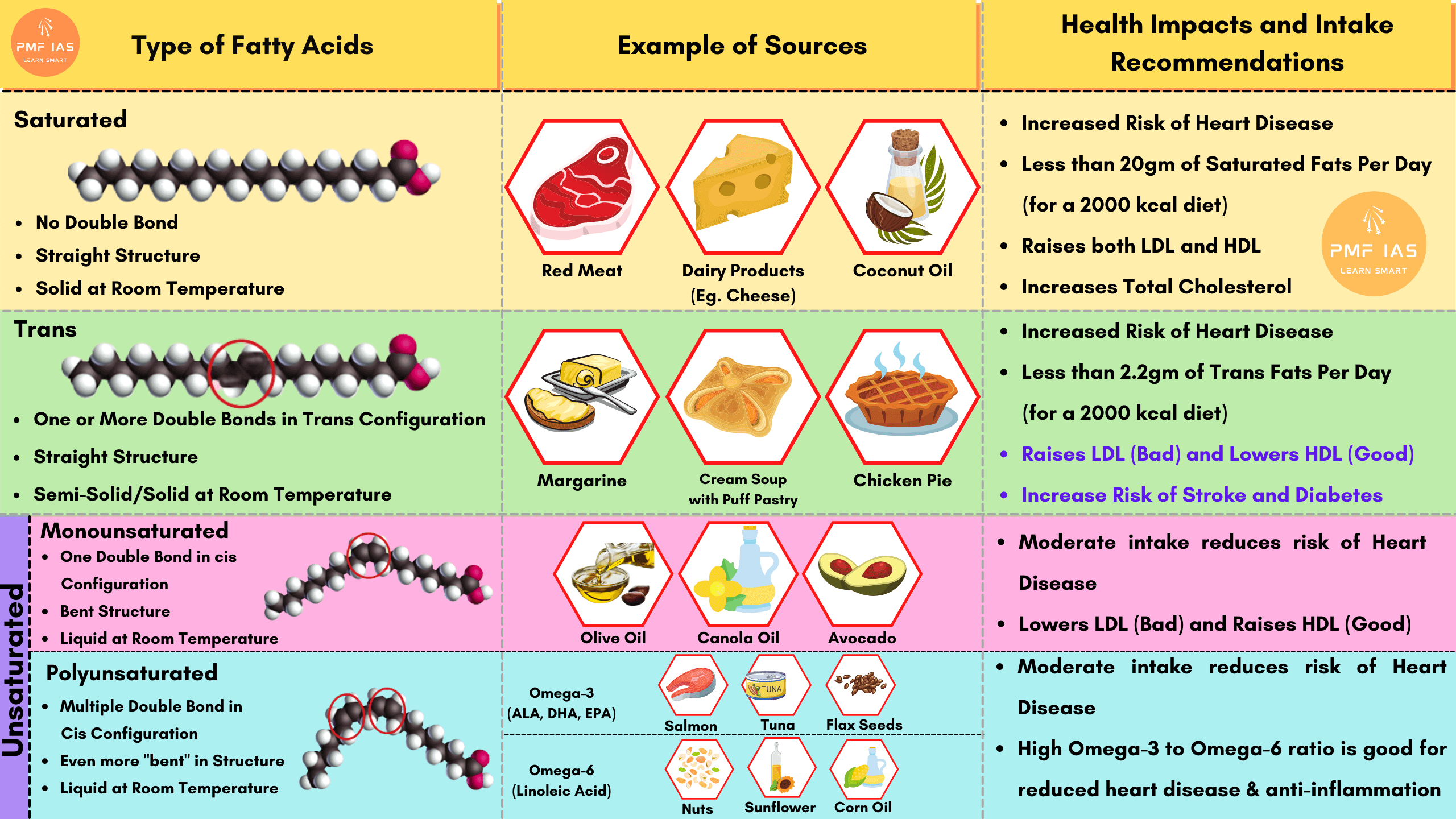
Fatty acids can be classified into:
Saturated
Trans
Monounsaturated (MUFA)
Polyunsaturated (PUFA)
CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS
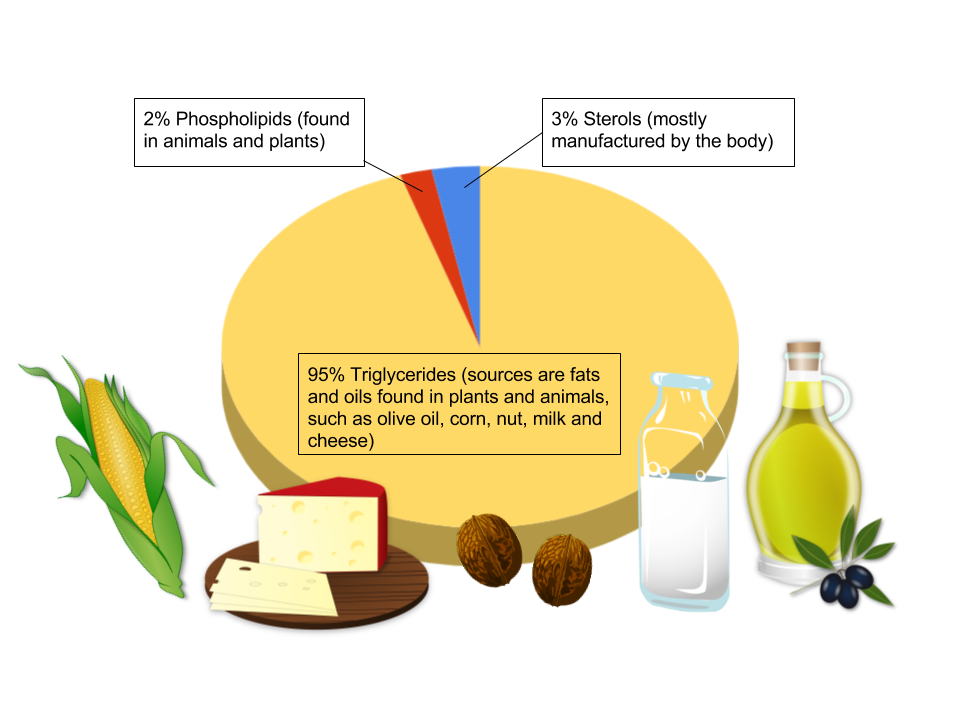
SIMPLE LIPIDS: These are fatty acids esterified with alcohol. This includes triglycerides, waxes, and sterols.
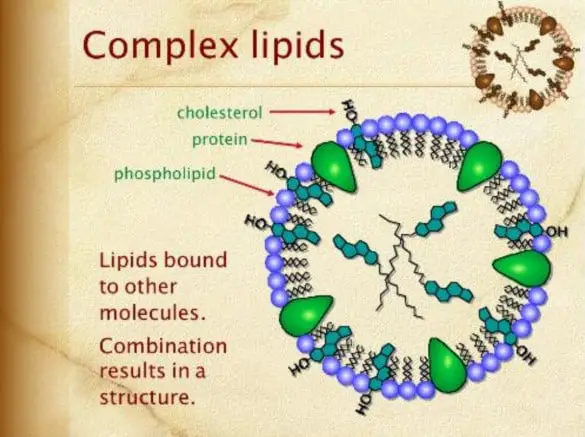
COMPLEX LIPIDS: These are lipids which are fatty acids with alcohol but with additional prosthetic groups. This includes phospholipids, glycolipids, and lipoproteins.
Speaking of lipoproteins;
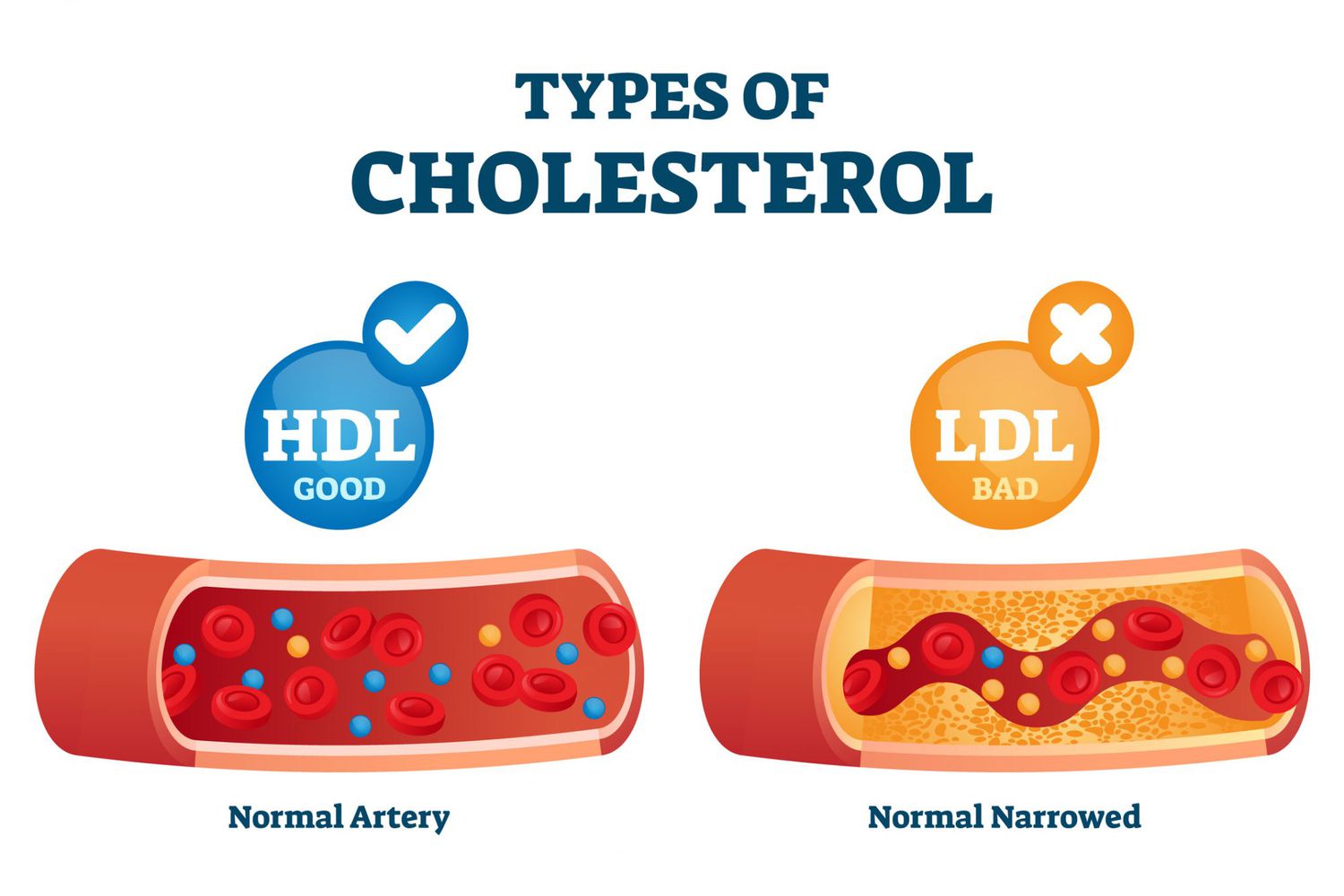
High Density Lipoproteins (HDL), which is known as good cholesterol,
Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL), which is known as bad cholesterol, cause toughening of our veins that compromises our health.

Therefore, our instructor reminds us that we need to be meticulous about what we are eating.
DERIVED LIPIDS: These lipids are the derivations of simple and complex lipids. This includes fatty acids, steroids, cholesterol, and ADEK vitamins.
How important are lipids in the food industry?
Fats improve the nutritional quality of food and give it the desired body and texture that adds satisfaction to consumer cravings since it imparts a distinct flavor to food and induces feelings of satiety or hunger loss. In other words, lipids contribute to texture, flavor, nutrition, and caloric density, all of which are key aspects of food quality. Since the beginning of food research, lipid alteration has been a primary focus in food industry.

Comments
Post a Comment